Non stick improvements in plastic and food processing machines
Lunac 1, and to some extent Lunac 2+, belong to the most effective, hard non-stick coatings minimizing sticking or degradation problems in baking machines and more specifically die-line and melt-fracture problems in plastic processing machines. Mold release in particular is highly influenced by the surface micro structure |
(e.g. orange skin and surface energy). However, melt flow is less affected by the surface energy than by the smoothness of the surface. Mobility of e.g. nano-particles in (modern) plastics is much improved in contact with very smooth surfaces (note: Lunac 1 can pretty easily be polished to very low surface roughnesses: Ra < 0.005 µm (0.0002 mil)). |
The positive effect of low surface energy
Generally, materials with lower surface energy tend to stick less to other materials. The most prominent effect of low
surface energy is the ease to be separated from other (covering) materials
and consequently to be cleaned. See also: melt conveyance directions.pdf
|
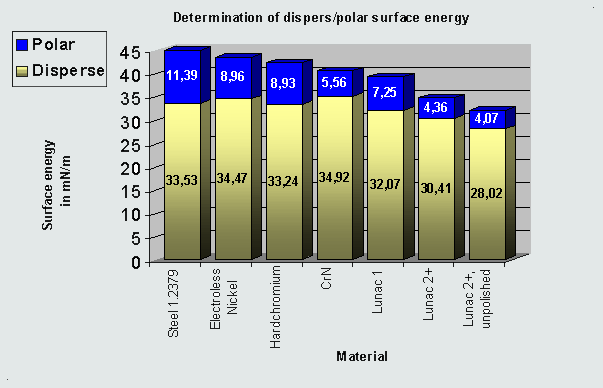
Diagram 1: The polar and disperse (=non polar, e. g. dominant in polyolefins) surface energies of various materials. Measured by the department of product engineering at the university of Duisburg (Germany). |
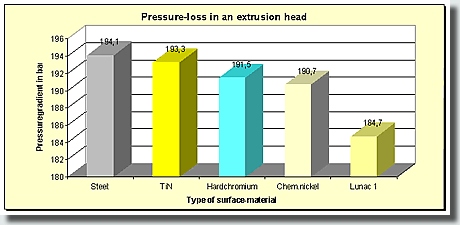
Diagram 2: The melt flow improvement capability (pressure gradient reduction) of various materials and coatings has been determined by a die head test of a plastic processing machine manufacturer. The plastic used was LDPE Lupolen 5021 at 18.33 Kg/h. |
The positive effect of high surface smoothness on melt flow
The influence of low surface energy is often over- estimated in melt flow systems. In-depth research by department of product engineering at the university of Duisburg revealed the dominant influence of surface smoothness. Further melt- flow improvement can be obtained |
by surface-roughness enhancement to very low values: e.g. Ra <0.005 µm / .0002mil. See diagram below. Even so, pollution control and product release are determined to a large extent by the surface energy and surface chemical (inert) behavior. |
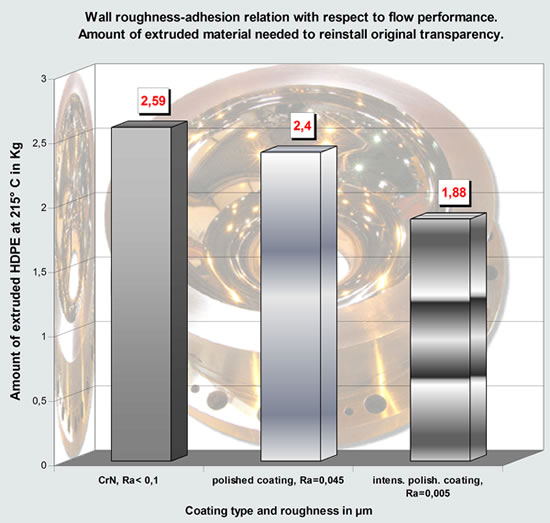
Diagram 3. This diagram displays the amount of administered transparent HDPE needed to acquire the same transparency after pigmented HDPE was administered before. The Lunac 1 coating can be polished to the last indicated extreme low value. |
Additional orange skin non-stick effect
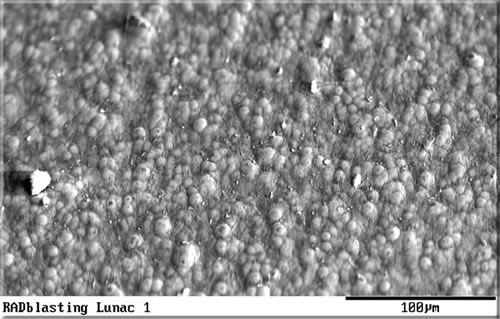 |
Figure 2: SEM picture of 'RAD Lunac 1'. Lunac 1 applied to a special bead blasted basic structure nucleates in just the right way to develop this ideal 'rounded' micro structure. This structure can improve the non- stick effect even further (especially in the case of perpendicular product release). Sometimes (in the case of rollers) the non stick effect can outperform even a PTFE based systems. The average roughness of this surface will be approximately 0.60 µm (0.024 mil).

Figure 3: This extrusion die with integrated filter disk has been coated with a corrosion-resistant non-stick Lunac 1 coating. Lunac 1 proved to be the most reliable way of minimizing problems with melt conveying, burned particles, edge build-up and melt fracture. The major advantages compared to PTFE based coatings are the hardness and 100% bond to the substrate. In addition the use of very expensive corrosion- resistant nickel alloys was rendered unnecessary in this case.

